Earth Day is less than a week away with this year’s theme of “Restore the Earth.” Earthday.org expounds on it by saying, “Together, we can prevent the coming disasters of climate change and environmental destruction. Together, we can Restore Our Earth.”
It is a fitting theme after the World Meteorological Society (WMO) declared 2011-2020 as the hottest year on record. Ocean heat is also hitting record levels due to greenhouse gas emissions. WMO Secretary-General Prof. Petteri Taalas explained, “In 2020, the annual Arctic sea ice minimum was among the lowest on record, exposing Polar communities to abnormal coastal flooding, and stakeholders such as shipping and fisheries, to sea ice hazards.” In a Panahon TV feature, PAGASA Hydrologist Rosalie Pagulayan warned that excess ocean heat may also fuel stronger tropical cyclones (bagyo). “Warmer oceans result in more evaporation. When there’s more moisture in the atmosphere, this could lead to intensified tropical cyclones. This means stronger rains, storm surges, and the possibility of tornadoes. Coastal communities will be inundated even those that do not usually experience floods.”
 Warmer oceans lead to intensified tropical cyclones. (Photo by Ricardo Esquivel from Pexels)
Warmer oceans lead to intensified tropical cyclones. (Photo by Ricardo Esquivel from Pexels)
As the planet heats up, more climate-related disasters occur. The United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR) reported that in the last 20 years, floods have doubled while storms increased by almost 40 percent. Major increases were also observed in droughts, wildfires and extreme temperature events.
Volcanic Eruptions and Earthquakes
The Philippines sits in the Pacific Ring of Fire, an area that experiences the most number of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. But according to this article, climate change might also have an effect on such disasters. It mentions a study that links small earthquakes to typhoons in eastern Taiwan, suggesting that decreased atmospheric pressure, which comes with typhoons, may cause earthquake faults to loosen and create tremors.
Meanwhile, a study from the University of Miami proposes that tropical cyclones and earthquakes are connected. It suggests that excess rainfall leads to landslides, which in turn reduces the weight on the fault below the earth’s crust, causing it to be more volatile.
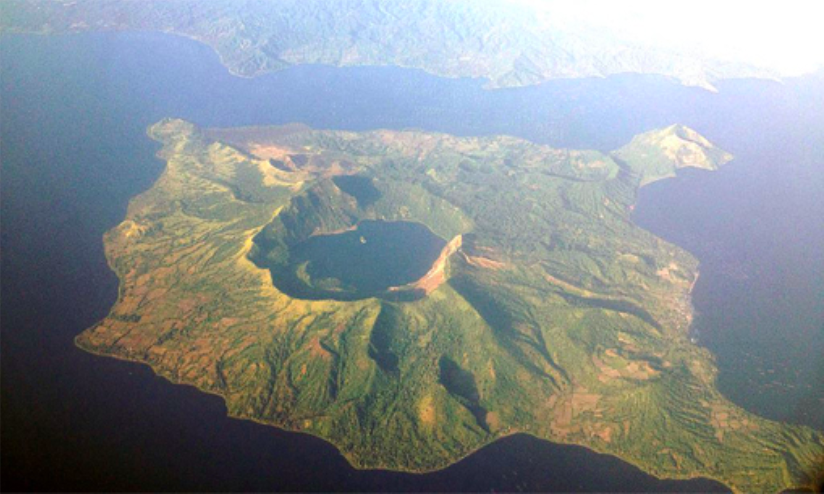 Taal Volcano is currently at Alert Level 2 according to PHIVOLCS.
Taal Volcano is currently at Alert Level 2 according to PHIVOLCS.
But how about volcanic eruptions? With Taal Volcano in Batangas currently at Alert Level 2, and its January 2020 eruption still fresh in our minds, should we be worried about climate change stimulating volcanic activity? The same article mentions the possibility of heavy rains triggering eruptions of the Soufrière Hills in Montserrat, and seasonal changes affecting Pavlof Volcano in Alaska.
However, in a Panahon TV interview, Dr. Renato Solidum Jr, officer-in-charge of the Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, and undersecretary for Disaster Risk Reduction and Climate, stated that global warming has no effect on earthquakes and current volcanic activities in the country. “Volcanic eruptions are caused by magma beneath the earth, and not by the Sun,” he explained in Filipino. “The same goes for earthquakes, which are caused by fault movement. This energy pushes the plates around the fault.”
But Solidum was quick to stress the fatal combined effects of volcanic eruption and extreme rainfall. “Because of global warming, evaporation is sped up, causing more rainfall. When a volcano has just erupted and is followed by rain, the water combines with the spewed-out ash and becomes lahar.” This was exactly what happened when Typhoon Diding followed the Pinatubo eruption in 1991, causing lahar attacks in Pampanga, Tarlac and Zambales, and burying entire towns.
Heavy rains can also exacerbate earthquake impacts. “Heavy rains can already cause landslides,” said Solidum. “But if an earthquake occurs while it’s raining, there might be stronger and more frequent landslides. Many more people will be affected.”
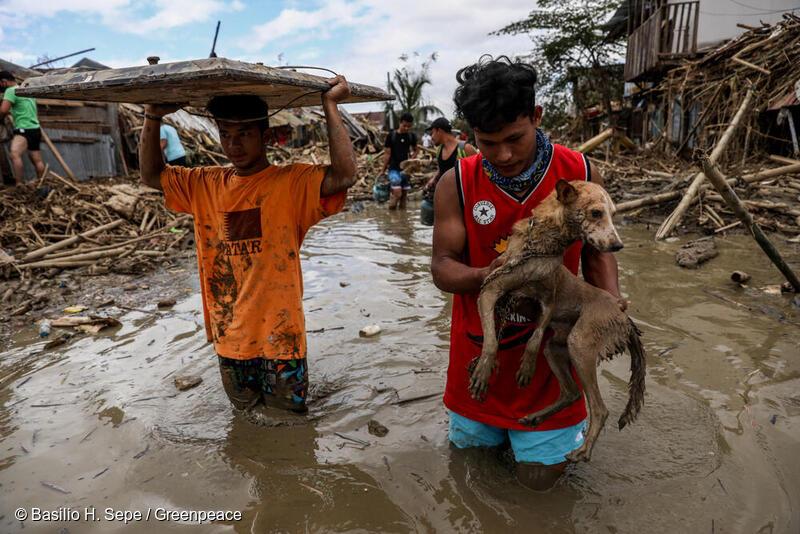 Residents in Rizal wade through flood caused by Typhoon Ulysses in November 2019
Residents in Rizal wade through flood caused by Typhoon Ulysses in November 2019
Environmental Care is Disaster Preparedness
Though geologic events such as earthquakes and eruptions happen naturally with or without climate change, Solidum explained how manmade activities can worsen their impacts. “Landslides occur in steep places or those with soft ground. Destroying our mountains through deforestation or housing developments leads to faster erosion and lowland flooding. The eroded soil along with improper waste disposal fill up our rivers and drainages, also causing floods.”
Solidum recalled the landslide that occurred in a subdivision in Antipolo, Rizal in 1996, which caused over 300 buried houses and 60 deaths. “The landslide was traced to the ground being disturbed during development. When heavy rains fell, the already loosened ground eroded. The disaster was human-influenced. That’s why houses shouldn’t be built on stiff slopes. The improper placement of septic tanks and drainages can also cause soil erosion.”
More recently, Cagayan province experienced massive floods after the onslaught of Typhoon Ulysses in November 2020. Though fingers were pointed at Magat Dam’s release, environmental groups also cited quarrying and illegal logging in the Sierra Madre mountain range as a major cause of the disaster. Cagayan Governor Manuel Mamba also faulted the heavy silt in Cagayan River for causing floods that resulted in 29 deaths.
Though it is vital to prepare for disasters with go bags and other preventive measures, Solidum stated that environmental care is just as important. “Protecting our environment is equivalent to caring for our communities and ourselves, so we can better prepare for natural hazards. These hazards become more fatal if we don’t care for our environment. Environmental care should be part of our disaster preparedness.”
Read up on how plastic pollution harms our health and environment, and take our quiz to find out how much of a zero-waste advocate you are.
Agay Llanera
An hour before midnight on October 26, 1978, Super Typhoon Kading was at its peak in the country, bringing torrential rains that caused the water level at Angat Dam to swell. Because stored water, when reaching a critical high level, might cause dam structures to break, the National Power Corporation (NPC) opened all its three floodgates to 8 meters. As the rains continued to pound, adding to the dam’s water level, NPC decided to further open the floodgates to its maximum height of 14 meters by 6 a.m. the next day.
This result was a catastrophe. With the sudden dam release, several towns in Bulacan near Angat Dam was instantly flooded. But the damage in houses, farms and working animals amounting to millions of pesos was not the only tragedy; with the dam’s spillways being opened without prior warning while residents were asleep, almost 200 people died in the sudden floods.
Civil suits were filed against NPC. Complainants all attested that they had not been warned of the maximum water release. Lives could have been saved if the dam release operation was done earlier and more gradually, and if there were proper communication among the sectors involved. In 1993, the suit was won, and NPC settled by giving 5 million pesos to families of those who had died.
But the tragedy was a wake-up a call to the government, which recognized the protocol gaps in dam release. In 1983, it began the Flood Forecasting and Warning System for Dam Operation. Implementation began in 1990, while the system became fully operational in 1992. The project led to the establishment of the PAGASA Data Information Center, flood forecasting and warning systems in both PAGASA and dam offices, hydrological stations, warning posts, and repeater and monitoring stations.
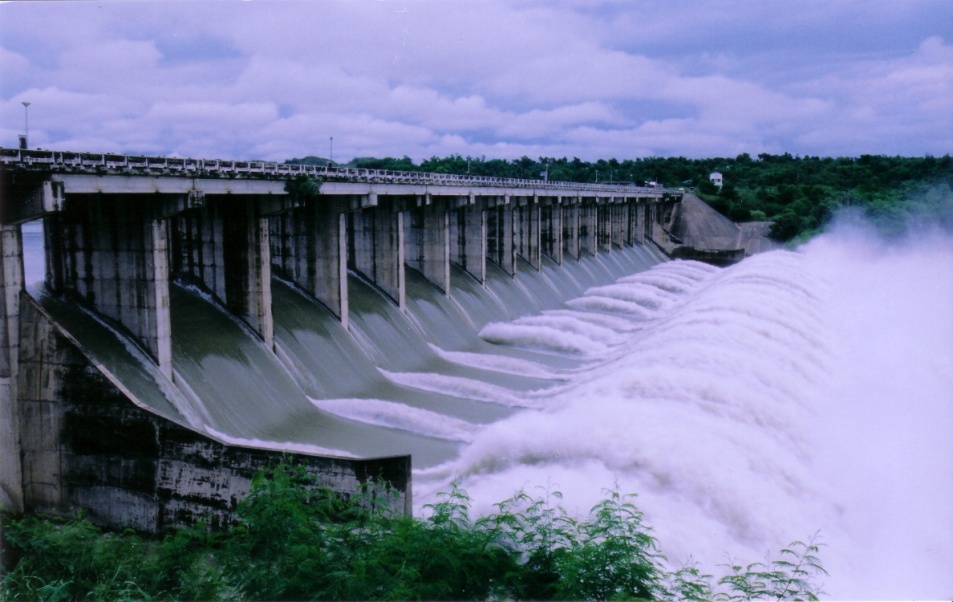

MARIS Dam in Nueva Ecija releases water (photo courtesy of NIA-Magat River Integrated Irrigation System)
Giving a dam(n)
PAGASA aims to manage the flooding risk caused by dams with its daily-updated products and services:
- Basin Daily Hydrological Forecast
- Flood bulletins
- General Flood Advisories (GFA) – Regional
- Status of Monitored Dams
Rosalie Pagulayan, a hydrologist at PAGASA, emphasizes the importance of risk management in harnessing the full potential of our dams. “Major dams are multipurpose,” she says. “They generate power, irrigate farms, provide potable water and controls flooding. During the rainy season, the dam stores excess water, keeping it from inundating the rivers and communities.” Angat Dam, in particular, provides 97% of Metro Manila’s water requirements, and irrigates 31,000 hectares of farmlands in Pampanga and Bulacan.
Though dams are meant to prevent flooding, extreme weather events that bring massive rains can force dam operators to conduct water releases.
But even the frequency of tropical cyclones in our country is a double-edged sword. “Many complain about the inconvenience of the rainy season, but upon studying our climate, a former PAGASA director was able to determine that 50% of our rain comes from tropical cyclones. If we don’t have tropical cyclones, our water supply suffers. Other weather systems are also important; the northwest and southwest monsoons bring 38% of our rain, while the ICTZ [intertropical convergence zone] brings 12%.” She adds that rains are important in crop irrigation and pushing out atmospheric pollution.
Pagulayan, who has been working in PAGASA for 15 years, says that there are protocols before spillways are opened. “Even before a typhoon comes, we predict how much rainfall it will bring. We give the data to the different dam offices, which compute the expected increase in water levels. To accommodate the incoming rain, the dams conduct pre-release—but only according to the river’s capacity to prevent flooding.” She adds that aside from measuring the amount of rain in the watershed, PAGASA also measure the rain’s impact. “There’s a warning post from dam offices before they release water. There’s ample lead time, so for example, if they’re opening the gates at 4 p.m., they warn residents as early as 10 a.m. so they can prepare.”
How flooding risks can be better managed
In other parts of the world, river systems span countries, such as the Brahmaputra River, which comes from India but flows downstream to Bangladesh. The famous Danube River also comes from several European regions. Such a situation calls for strong international coordination when the source of the river swells, and flows down to various countries and territories in low-lying areas.
But Pagulayan says this is not a problem in our country. “We are blessed with big river systems. We manage our own rivers, and solely benefit from them. Our rivers traverse through various municipalities, provinces and even regions.”
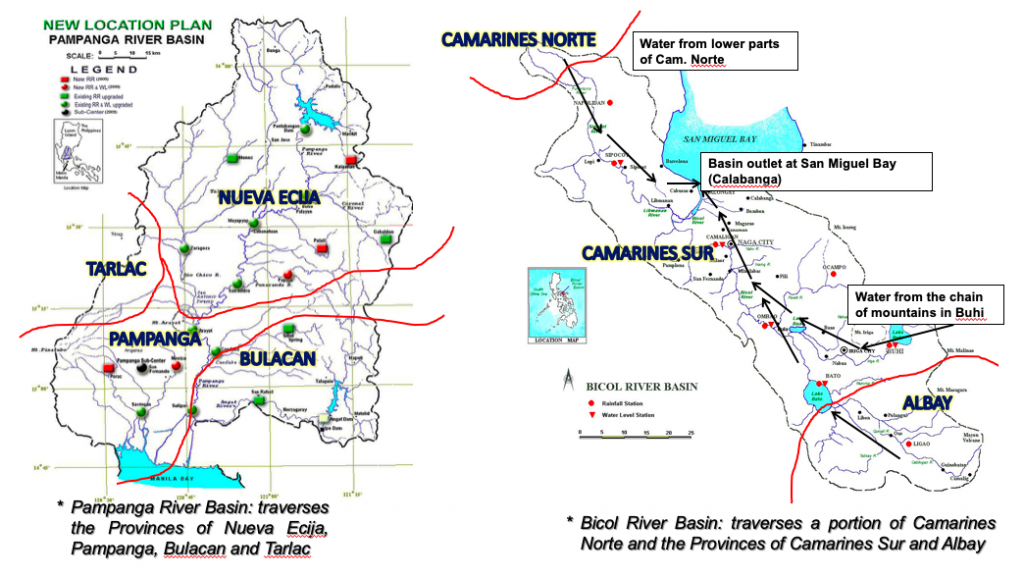
In the left graph above, Pagulayan shows how water from Nueva Ecija flows down to the Pampanga river basin, and contributes to a portion of Tarlac and Bulacan. “Our river systems encompass a lot of areas so disaster managers in these zones should be seamless in their communication and info-sharing.”
Meanwhile, as shown in the right graph above, water from the Bicol river basin comes from Albay, Camarines Norte, and mostly Camarines Sur. “But the Camarines Norte source is very important because rains are strong there, and because of its elevation, water flows down very fast,” shares Pagulayan. “All these rivers are owned by the Philippines. We don’t share them with other countries or regions. We are the only ones who can harness their potential.”
In areas that receive a lot of rain, dams and water reservoirs are built in mountainous areas, which can hold excess water. But watershed deforestation is an issue, leading to its decreased capacity for water storage. This may lead to flooding during the rainy season, and water supply shortage during the hot and dry season.
Risks also increase when people build their homes and livelihoods near waterways and flood plains. “They may find it convenient to set up livelihoods that require water, such as farms, in those areas, but once water is released, their safety is compromised,” explains Pagulayan. “Flooding also negates development efforts, and destroys agricultural products and infrastructure. But the worst risk of all is the loss of lives.”

MARIS Dam’s spillway in Nueva Ecija (photo courtesy of NIA-Magat River Integrated Irrigation System)
Moving forward
To foster good relations with dam offices and local government units (LGU), PAGASA regularly conducts information and education campaigns, public information drives, and communication drills. “For every disaster, the challenge, I think, is communication, so this is what we constantly develop. We can’t stop; it has to be continuous so we can improve,” Pagulayan shares.
By practicing and strengthening the information flow from PAGASA down to the regional and municipal levels, data accuracy is ensured, allowing LGUs to map out action plans to lessen flooding impacts. “We learn from every experience how to convey data and information. We are open to change and we adjust our activities, so we can improve both our services and community action,” ends Pagulayan.
Communities can also mitigate risks by knowing what to do before a tropical cyclone arrives and causes flooding.
The country remains storm-free but heavy rains have caused massive floods in various areas in Cagayan.
This is caused by Tail-end of a Cold Front – an extension of a weather system that forms when the cold air mass dominates the warm air mass, causing interaction and rains.
Due to the inclement weather, evacuation has been ordered, classes have been suspended and flights have been cancelled today. Here are some images of the floods in Luzon:





Photos from Cagayan Provincial Information Office.
Sendai, Japan- The Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations (FAO) has released a new study stating that 22% of damages from natural disasters, such as floods, droughts and storms, have an impact on agriculture.
This comes from a report from FAO, consisting of 78 post-disaster needs assessments in 48 developing countries spanning the 2003-2013 period.
FAO Director-General José Graziano da Silva emphasized the importance of the agricultural sector, stating that “it encompasses is not only critical for our food supply, it also remains a main source of livelihoods across the planet. While it is a sector at risk, agriculture also can be the foundation upon which we build societies that are more resilient and better equipped to deal with disasters,”
He noted that there is a need to prioritize Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) in the agriculture sector as studies have shown that for every one dollar spent on DRR, as much as four dollars are returned, in terms of avoided or diminished impacts.
A new facility focusing on how countries can be more resilient before disasters occur was launched by the FAO, which would be focusing on technical training and support for farmers and fisherman from rural communities.
New Technologies Supporting DRR
Having learned lessons from the 2011 earthquake, the BOSAI Industry fair showcased various technologies for DRR. The Japan Bosai Platform is a platform and catalyst for multi-stakeholders to pursue a holistic approach in reducing disaster impacts around the world.
Among the various developments was the use of hybrid cars as energy source during emergencies and disasters. Household appliances such as microwave ovens, lamps and rice cookers can get power from the vehicle.
Model of the Tsunami Evacuation Tower
New structures such as the creation of Tsunami Evacuation Towers were also showcased at the fair.
Vegetable juice as emergency food
Practical Emergency items such as emergency kits and emergency food were also presented at the fair.


